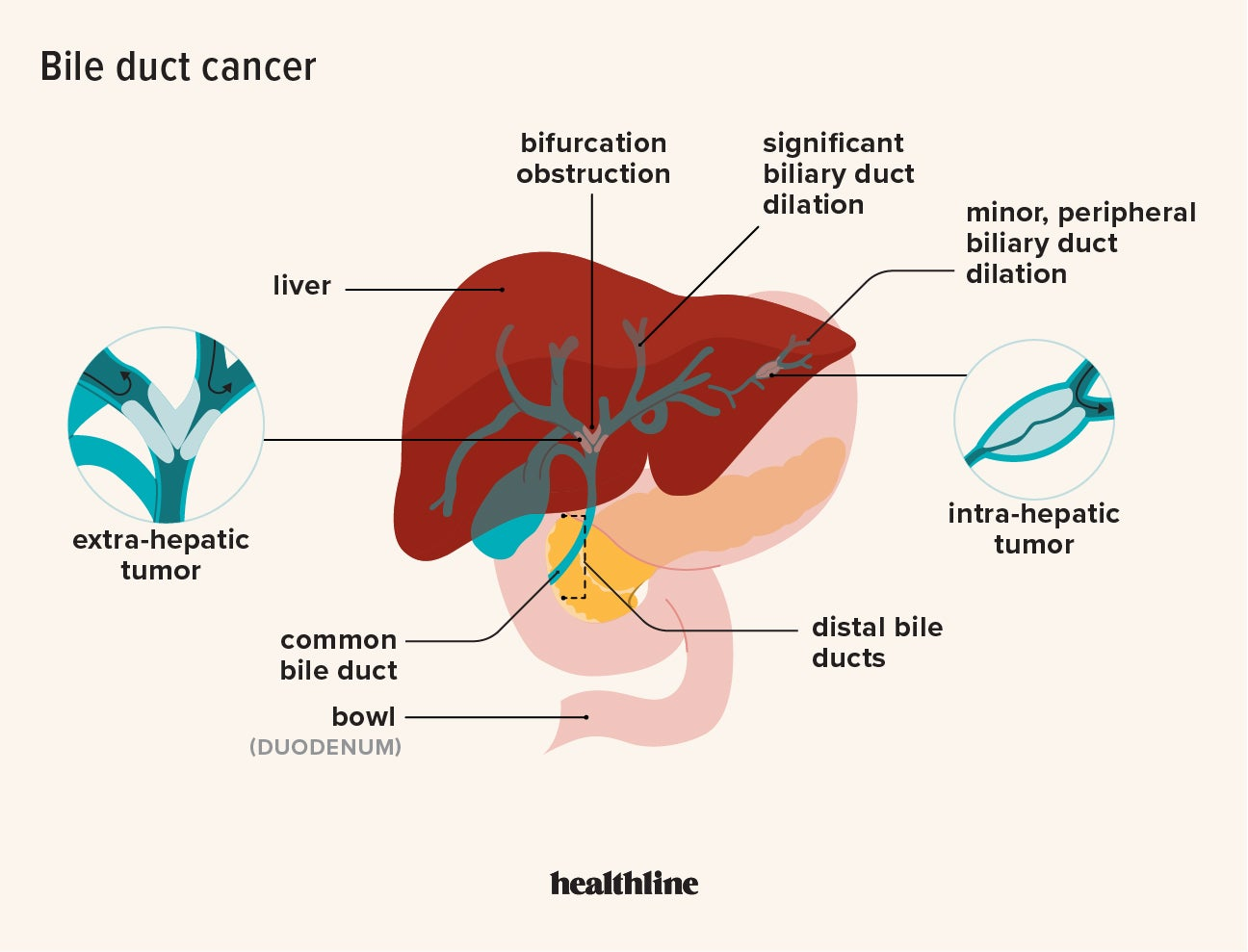
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a critical area of research that highlights the complex relationship between bile acids and serious liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies reveal that when bile acids become dysregulated—due to an imbalance in their production—they can initiate pathways leading to liver injury, inflammation, and cancer. The liver’s ability to produce and manage bile is essential for maintaining liver health, but disruptions can trigger severe consequences. A key discovery in this field is the role of the YAP FXR signaling pathway, which, when altered, contributes to the overproduction of bile acids and thus accelerates the progression to liver cancer. As scientists continue to investigate these mechanisms, there is hope for developing new treatments aimed at restoring bile balance and improving outcomes for patients with liver cancer.
The phenomenon of bile acid dysregulation is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the development of liver malignancies. Known as hepatic cancers, these diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, can stem from issues related to bile production and metabolism. With bile acids acting not just as digestive agents but also as important regulators of metabolic processes, their imbalance poses risks to liver function. Current research is focused on cellular signaling pathways, especially involving YAP and FXR, that mediate bile homeostasis and could offer insights into new therapeutic strategies. Understanding how these metabolic disturbances contribute to liver health is crucial for devising effective interventions for liver cancer.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Connection to Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance can significantly impact liver health, leading to acute issues that manifest as serious conditions, such as liver cancer. The liver produces bile, a substance crucial for digesting fats and absorbing fat-soluble vitamins. When bile acids become imbalanced, they accumulate in the liver, resulting in harmful effects like inflammation, fibrosis, and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This imbalance is particularly concerning as HCC is the most prevalent form of liver cancer, highlighting a critical pathway in how liver dysfunction paves the way to cancer progression.
The study led by Yingzi Yang sheds light on the molecular mechanisms behind this bile imbalance, specifically how the YAP and FXR pathways interact. YAP, typically known for promoting cell growth, surprisingly inhibits the FXR, a vital receptor in maintaining bile acid levels. This process leads to overproduction of bile acids, causing liver damage over time. By targeting this pathway, potential treatments could emerge that might halt or reverse liver cancer progression.
The Role of YAP in Liver Cancer Pathogenesis
YAP (Yes-associated protein) has emerged as a pivotal player in liver cancer pathology, specifically in the context of bile acid metabolism. Previous perceptions of YAP primarily revolved around its role in promoting cell proliferation. However, recent discoveries reveal that YAP has a dual function—it acts as a repressor that modulates FXR activity. This repressive action on FXR leads to bile acid dysregulation in the liver, contributing to the onset of liver cancer. Understanding this complex interplay between YAP and FXR is essential for developing targeted treatment strategies.
The potential for YAP inhibitors to serve as therapeutic agents is particularly exciting for researchers and clinicians. By blocking YAP’s repressive effects, it may be possible to reinstate normal FXR function, thus promoting bile acid homeostasis. This could ultimately reduce liver inflammation and damage, presenting a promising avenue for preventing or treating hepatocellular carcinoma before it progresses to more advanced stages.
Bile Acids and Their Hormonal Functions in Metabolism
Bile acids do more than facilitate digestion; they also function as signaling molecules that regulate various metabolic processes. This hormone-like action affects not only lipid metabolism but also glucose homeostasis and energy expenditure. Bile acids interact with several receptors, including the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), influencing how the body processes nutrients. The discovery that bile acid imbalance can lead to serious conditions like liver cancer underscores the importance of maintaining healthy bile acid levels.
In light of recent findings, there is growing interest in exploring the therapeutic potential of bile acids and their analogs. Medical researchers are keen to leverage the beneficial aspects of bile acids, particularly their role in modulating various metabolic pathways. By integrating advances in bile acid research with liver health preservation strategies, future therapies may not only address symptoms but also target the root causes of liver diseases and cancer.
Implications of Research on Liver Health and Cancer Treatment
The implications of the research conducted by Yang and her team extend far beyond basic science, offering insight into innovative treatment options for liver cancer. By identifying the dysfunctions in bile acid metabolism linked to YAP and FXR, clinicians could develop targeted therapies that not only focus on cancer treatment but also on restoring liver health. This holistic approach may help to mitigate the risk factors contributing to liver cancer, offering a proactive strategy in cancer care.
Moreover, as more connections are made between bile imbalance and liver cancer, screening and early intervention strategies could improve patient outcomes. Simple changes to diet and lifestyle, along with pharmacological interventions to restore bile acid balance, may become pivotal in preventing the advancement of hepatocellular carcinoma. The ongoing research is a crucial step toward more comprehensive strategies for liver disease management.
Investing in Research for Bile and Liver Health
Investing in research dedicated to understanding bile acids and liver health is crucial for advancing the field of hepatology. The complexity of liver functions and their interrelation with bile acids necessitates further exploration of the molecular signaling pathways involved. Studies like the one led by Yingzi Yang are paving the way for novel therapeutic interventions that can address the root issues leading to liver cancer and other diseases. Without sufficient funding and resources, many of these promising avenues may go unexplored.
Collaboration between research institutions, universities, and healthcare providers can accelerate the pace of discovery in this vital area. By disseminating findings beyond academia and into clinical applications, patients suffering from liver-related conditions may benefit from cutting-edge treatments designed from the latest research. This partnership approach may lead to innovative solutions that not only target liver cancer but also promote overall liver health across diverse populations.
Exploring Genetic Factors in Liver Cancer Development
Genetic factors play an integral role in the development of liver cancer, particularly through their influence on bile acid metabolism. Genetic mutations affecting bile production and metabolism can precipitate conditions that lead to hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding these genetic underpinnings could be key to identifying individuals at risk and developing personalized treatment plans. Furthermore, studying gene-environment interactions can provide insight into how lifestyle choices may mitigate or exacerbate these risks.
As research continues to unravel the genetic landscape surrounding liver cancer, potential targets for gene therapy could emerge. These therapeutic strategies could aim to correct malfunctioning genes or introduce new, healthy genes to restore normal liver function. With a comprehensive understanding of how genetics interacts with bile acid metabolism, the fight against liver cancer could take transformative steps toward prevention and treatment.
Lifestyle Changes to Promote Healthy Liver Function
Lifestyle modifications are essential for promoting healthy liver function, particularly when it comes to maintaining a balanced bile environment. Diet plays a pivotal role; incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and fiber can support bile production and overall liver metabolism. Additionally, hydration is critical for ensuring the proper flow of bile and preventing imbalances that can lead to liver disease and cancer.
Regular physical activity also contributes to liver health by supporting metabolic processes and reducing the risk of obesity—a significant risk factor for liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Patients who actively engage in healthy lifestyle choices can mitigate their risk of developing liver cancer and lean into preventative measures that enhance the quality of their liver function. By focusing on prevention through lifestyle, the incidence of liver cancer can be significantly lowered.
The Future of Pharmacological Treatments in Liver Cancer Management
Pharmacological advancements hold immense promise for improving liver cancer management, particularly through the use of drugs that target bile acid regulation. The ongoing exploration of FXR agonists exemplifies the potential for drugs that can restore bile acid homeostasis. By enhancing the function of FXR, these therapies could revolutionize how liver cancer is treated by directly addressing one of the underlying factors of the disease—bile acid imbalance.
Additionally, developments in precision medicine provide opportunities for tailoring treatment approaches based on individual physiology and disease progression. By combining traditional therapies with new pharmacological interventions aimed at correcting biliary dysregulation, the field of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment could evolve into a more integrative and effective paradigm. This holistic focus on the biochemical environment of the liver is crucial for combating liver cancer more effectively and sustainably.
Expanding Knowledge on Bile Acids and Their Metabolism
The expanding body of research surrounding bile acids and their metabolism continues to unveil critical information regarding liver health and disease. As scientists deepen their understanding of how bile acids signal cellular functions, they can also explore new ways to combat liver diseases from a metabolic perspective. Insights from studies examining pathways like YAP and FXR are paving the way for research focused specifically on bile acid therapeutic interventions.
Future investigations into bile acids may also reveal novel biomarkers for liver diseases, which can lead to earlier detection and intervention strategies for at-risk populations. By comprehensively studying bile acid metabolism and its implications for liver cancer, the healthcare community can fortify its approach to liver health, improving outcomes for those affected by liver conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is closely linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruption in bile acid production can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are critical factors in the development of liver cancer. A recent study identified a molecular switch that, when altered, results in the overproduction of bile acids, contributing to the pathogenesis of HCC.
How do bile acids influence liver health in relation to liver cancer?
Bile acids play a significant role in liver health as they aid in fat digestion and act as hormones that regulate metabolic processes. An imbalance in bile acids can disrupt liver function, leading to conditions such as fibrosis and inflammation. These changes increase the risk for developing liver cancer, emphasizing the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis in preventing HCC.
What role does the YAP FXR pathway play in liver cancer and bile imbalance?
The YAP FXR pathway is crucial in regulating bile acid metabolism. YAP can inhibit the function of FXR, a key bile acid sensor, resulting in bile acid overproduction. This dysregulation can lead to inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately increasing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Targeting this pathway may provide new strategies for liver cancer treatment.
Can correcting bile acid imbalances help prevent liver cancer?
Yes, correcting bile acid imbalances may potentially prevent liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma. By enhancing FXR activity or promoting bile acid excretion, researchers aim to halt the damaging cycle of bile overproduction and inflammation, reducing the risk of liver cancer development.
What are the potential treatments for liver cancer linked to bile imbalance?
Potential treatments for liver cancer related to bile imbalance may include pharmacological solutions that stimulate FXR. These treatments focus on restoring bile acid homeostasis and preventing liver damage. Activating FXR, inhibiting YAP, and enhancing bile acid export proteins are promising strategies being explored for liver cancer therapy.
How does liver health relate to bile acid regulation in cancer prevention?
Maintaining optimal liver health is essential for effective bile acid regulation, which is crucial for preventing cancer. A healthy liver ensures proper bile production and metabolism, minimizing the risk of inflammation and fibrosis that can lead to conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Regular monitoring and interventions to correct bile imbalances can thus contribute to cancer prevention.
What factors contribute to bile acid overproduction and liver cancer development?
Factors that contribute to bile acid overproduction include disruptions in the regulation of the YAP FXR pathway, inflammation, and liver injury. These disruptions can lead to excessive bile accumulation, damaging liver tissue and increasing the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding these factors is vital for developing targeted liver cancer therapies.
How is bile acid homeostasis linked to hepatocellular carcinoma?
Bile acid homeostasis is critically linked to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as imbalances can lead to liver injury and inflammation. When the regulatory pathways, such as YAP and FXR, are disrupted, it can result in overproduction of bile acids, promoting the progression of liver damage and increasing the likelihood of developing HCC.
What are the implications of recent research on bile imbalance and liver cancer treatment?
Recent research highlights the potential for pharmacological interventions targeting bile acid metabolism to treat liver cancer. By focusing on the YAP FXR pathway and enhancing bile acid excretion, new therapies could emerge that not only address bile imbalance but also reduce the risk and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance of bile acids can trigger liver diseases including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common liver cancer. |
| Molecular Switch Identified | The study identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile, which may lead to new liver cancer treatments. |
| Function of Bile | Bile aids in the digestion of fats and serves hormone-like functions governing metabolic processes. |
| Role of YAP | YAP, a protein involved in cell signaling, promotes tumor formation while regulating bile acid metabolism. |
| FXR and Bile Acid Homeostasis | FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) is crucial for bile acid balance; YAP inhibits its function leading to liver damage. |
| Potential Treatment Solutions | Activating FXR or blocking YAP’s function may help reduce liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Implications | The findings point to pharmacological solutions that could enhance FXR function, offering hope for treatment. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is a significant discovery that sheds light on the mechanisms behind liver disease progression, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The research highlights the intricate role of bile acids and their regulation through molecular switches like YAP and FXR, opening avenues for potential therapeutic interventions. Addressing bile imbalance could lead to innovative strategies for treating liver cancer, emphasizing the critical need for further research in this area.