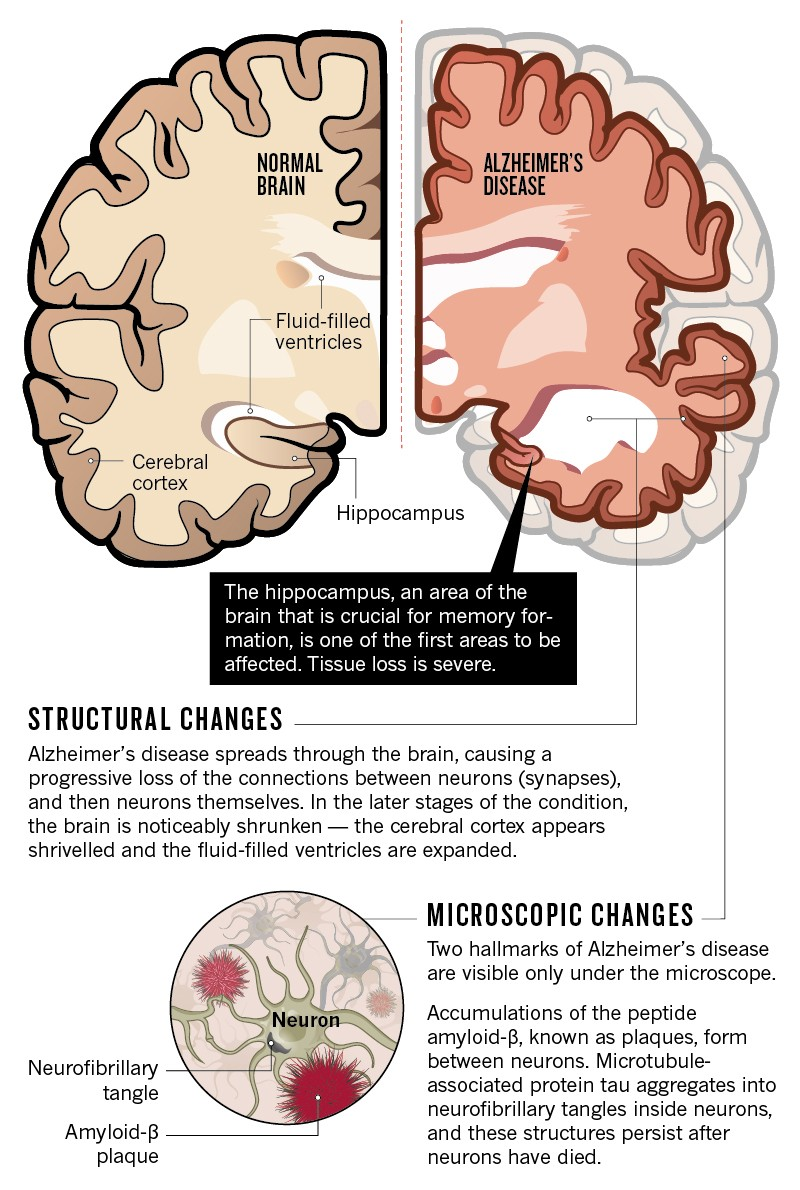
Age-related brain disease encompasses a range of conditions, including stroke and dementia, that significantly impact cognitive health as we age. Recent research highlights the importance of understanding modifiable risk factors that can help in preventing these debilitating diseases. For instance, managing blood pressure, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, and engaging in physical activity are crucial steps toward enhancing brain health and reducing dementia risk. The study also reveals that recognizing and addressing factors leading to late-life depression can be instrumental in comprehensive brain health strategies. By focusing on these modifiable factors, individuals can take proactive measures to safeguard their mental well-being and enhance their quality of life.
As we delve into the subject of age-related brain diseases, it’s essential to recognize the broader spectrum of cognitive decline and neurological disorders that affect our golden years. Terms such as cognitive impairment, dementia syndromes, and neurodegenerative illnesses encapsulate the challenges faced by many during late adulthood. Understanding the interconnectedness among these conditions sheds light on the importance of risk factor management in promoting brain health. With a holistic approach focusing on prevention strategies that address both physical and psychological well-being, we can effectively tackle issues like stroke, depression, and cognitive deterioration. Enhanced awareness and action towards these concerns not only improve individual health outcomes but also contribute to healthier aging.
Understanding Age-Related Brain Diseases and Their Common Risk Factors
As individuals age, the risk of developing age-related brain diseases such as dementia, stroke, and late-life depression increases significantly. These conditions do not exist in isolation; they are interconnected and share many common risk factors. Recent research has revealed that 17 modifiable factors can be altered through lifestyle changes, providing a proactive approach to enhancing brain health. By identifying these risk factors, we can better understand how to mitigate the risks associated with these debilitating conditions.
Among the identified risk factors, high blood pressure and kidney disease have the most pronounced impact on the likelihood of developing not only dementia and stroke but also depression in older adults. This revelation emphasizes the importance of regular health screenings and lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and engaging in regular physical activity. These changes can significantly contribute to better brain health, demonstrating that individuals have the power to influence their cognitive longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the modifiable risk factors for age-related brain disease that can help reduce dementia risk?
Research indicates that several modifiable risk factors can lower dementia risk associated with age-related brain disease. Key factors include managing blood pressure, controlling diabetes, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, engaging in regular physical activity, and having a balanced diet. Addressing these factors not only enhances brain health but also reduces the likelihood of developing other conditions such as stroke and late-life depression.
How does high blood pressure relate to age-related brain diseases like stroke and dementia?
High blood pressure is a significant modifiable risk factor for age-related brain diseases, including stroke and dementia. It can lead to the deterioration of blood vessels in the brain, increasing the chances of stroke and the onset of dementia. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medications can help protect brain health and reduce the overall risk of these debilitating conditions.
Can lifestyle changes help in preventing age-related brain diseases such as late-life depression and dementia?
Yes, lifestyle changes are crucial in preventing age-related brain diseases like late-life depression and dementia. Factors such as regular physical activity, a healthy diet, sufficient sleep, and social engagement play a vital role in maintaining brain health. Implementing these changes can significantly lower the risk of developing these conditions, enhancing overall quality of life as we age.
What role does social engagement play in preventing age-related brain diseases?
Social engagement is an essential modifiable risk factor for preventing age-related brain diseases, including depression and dementia. Engaging with friends, family, and community activities helps stimulate cognitive function and provides emotional support, reducing feelings of isolation that can contribute to late-life depression. Encouraging social interactions can, therefore, be a vital component in promoting brain health.
How does obesity affect the risk of age-related brain diseases like stroke and dementia?
Obesity is a well-recognized risk factor that increases the likelihood of developing age-related brain diseases such as stroke and dementia. Excess weight can contribute to high blood pressure, diabetes, and poor cardiovascular health, all of which are linked to a higher risk of neurological decline. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly help in mitigating these risks.
What is the Brain Care Score, and how does it relate to age-related brain disease prevention?
The Brain Care Score is a tool developed to assess and guide individuals in protecting their brain health by focusing on modifiable risk factors associated with age-related brain diseases. By evaluating lifestyle choices related to diet, physical activity, and other health metrics, the Brain Care Score helps individuals make informed decisions that can reduce the risk of conditions like stroke, dementia, and late-life depression.
What impact do cognitive activities have on the risk of age-related brain diseases?
Cognitive activities, including puzzles and reading, may have a protective effect against age-related brain diseases such as dementia. Engaging the brain in stimulating activities can promote cognitive resilience and is associated with a lower risk of disease. Therefore, incorporating mental challenges into daily routines can be beneficial for long-term brain health.
How can managing stress levels reduce the risk of age-related brain diseases?
Managing stress is crucial for lowering the risk of age-related brain diseases, including depression and dementia. Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on brain health, leading to cognitive decline. Implementing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and regular physical activity can enhance brain health and potentially prevent the onset of related conditions.
Why is understanding shared risk factors important for age-related brain disease prevention?
Understanding shared risk factors is essential for age-related brain disease prevention as it highlights the interconnections between conditions like stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. By addressing these overlapping risk factors, healthcare efforts can be more effective, simultaneously reducing the incidence of multiple diseases and improving overall brain health.
| Risk Factor | Impacted Conditions | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Common metabolic disorder affecting blood sugar levels. |
| Blood Pressure | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | High levels significantly increase risk for all three. |
| Kidney Disease | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Compromises overall health and increases brain disease risk. |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Indicator of long-term blood sugar levels. |
| Total Cholesterol | Stroke, Dementia | High levels are linked to increased brain disease risk. |
| Alcohol Use | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Excessive intake can negatively affect brain health. |
| Diet | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Nutritional choices play a vital role in brain health. |
| Hearing Loss | Dementia | Affects communication and cognitive function. |
| Pain | Depression, others | Chronic pain can lead to mental health challenges. |
| Physical Activity | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Regular exercise reduces overall health risks. |
| Purpose in Life | Depression, others | Having goals helps enhance mental vitality. |
| Sleep | Depression, others | Good sleep quality is essential for mental health. |
| Smoking | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Tobacco use has multiple negative health effects. |
| Social Engagement | Depression, others | Social connections are fundamental for well-being. |
| Stress | Depression, others | Chronic stress can harm mental health over time. |
| Depression | Others | Can co-occur and exacerbate other health issues. |
| Obesity | Stroke, Dementia, Depression | Excess weight can trigger numerous health problems. |
Summary
Age-related brain disease encompasses conditions like stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, which can significantly impact cognitive health. Recent research highlights 17 modifiable risk factors that could potentially lower these risks, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle changes in promoting better brain health. By addressing factors such as blood pressure, diet, and physical activity, individuals may significantly reduce their likelihood of developing these debilitating conditions. Understanding and modifying these risk factors can empower people to enhance their quality of life and delay the onset of age-related brain diseases.