Is Sugar Addictive? This intriguing question has sparked a significant debate among health experts and nutritionists alike. While research shows that sugar can trigger intense cravings and influence eating behaviors akin to addictive substances, it is important to clarify that sugar is not classified as an addictive drug. Yet, the effects of sugar on health are undeniable, especially in an age where processed sugars dominate our diets. With nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar consumed daily by the average American, understanding the dynamics of sugar cravings becomes essential for those looking to lead healthier lives and reduce sugar intake.
Exploring whether sugar possesses addictive properties leads us to a broader discussion about our dietary habits and the prevalence of sweeteners in modern diets. Many individuals experience overwhelming urges for sugary snacks, and this phenomenon can be likened to dependence on other substances. The notion of sugar as a potential addictive substance raises awareness of lifestyle choices, especially in relation to the processed foods saturating grocery shelves. This conversation emphasizes the impacts of sugary consumption on overall health and reveals the importance of making conscious efforts to manage dietary sugar. Whether termed as sweet cravings or sugar dependency, understanding this relationship is crucial in fostering healthier eating patterns in our daily lives.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
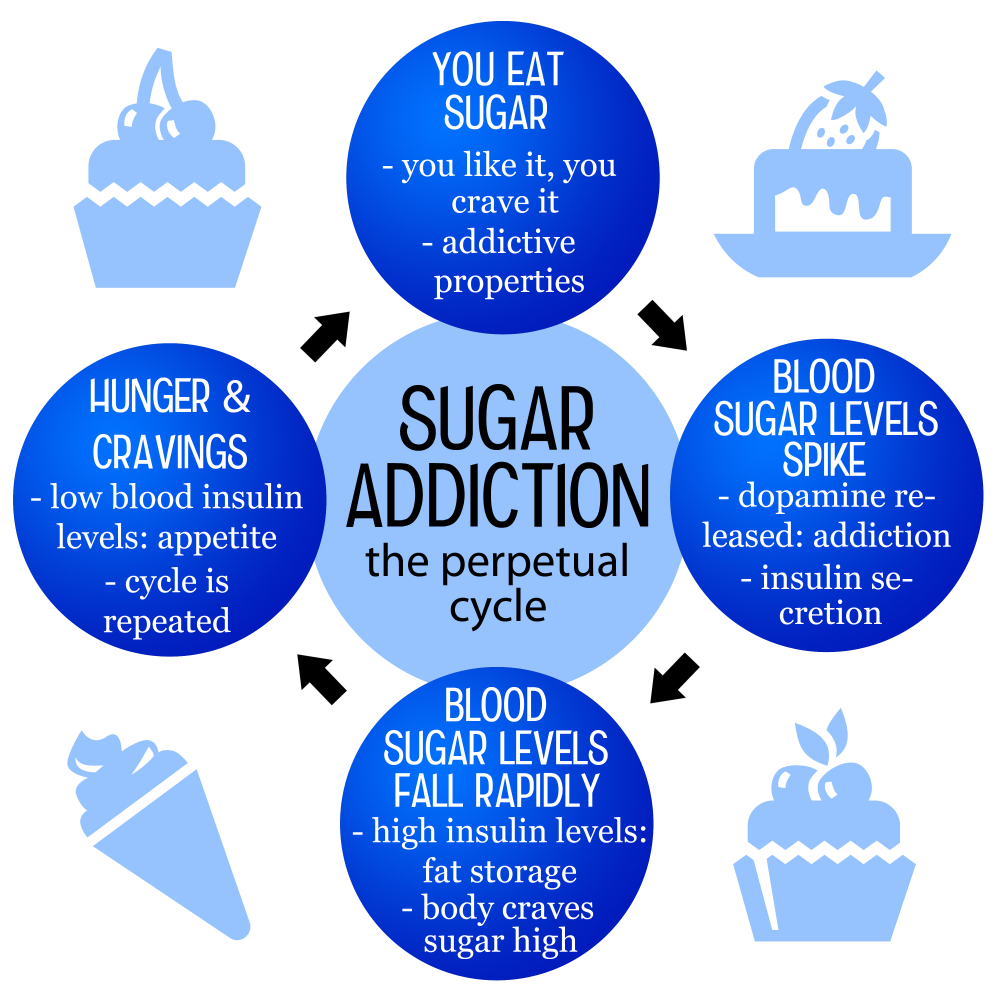
Sugar addiction is a term that often emerges in discussions about dietary habits and cravings. While sugar may not be classified as an addictive substance in the same realm as nicotine or alcohol, it can certainly trigger compulsive behaviors that resemble addiction. The reasons behind sugar cravings are multifaceted, involving physiological, psychological, and environmental factors. Many people find it difficult to resist sugary foods, especially those that are ultra-processed, which are engineered to enhance palatability and create a heightened desire for consumption. As nutrition experts suggest, this habitual intake of sugary foods can lead to significant health consequences, indicating that while sugar may not fit the strict definition of addiction, its effects on eating behavior are undeniable.
What makes sugar so appealing is not just its taste, but also the dopamine response it elicits in the brain. This reward system can drive individuals to seek out sugary snacks as a means of comfort or a way to cope with stress. Over time, this can develop into a pattern of excessive consumption, leading to an increase in health issues like obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. By understanding the concept of sugar addiction, individuals can take important steps toward managing their diet effectively, such as recognizing their reliance on sugar and being mindful of the types of foods they consume.
Effects of Sugar on Health
The effects of sugar on health are profound and far-reaching. High intake of processed sugars is linked to numerous health issues, including weight gain, increased risk of heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. When we consume sugar, especially in large amounts, our bodies experience rapid spikes in blood glucose levels, leading to energy crashes and increased cravings for more sugar. This cycle promotes a dependency that fuels unhealthy eating habits and ultimately harms overall health. The American Heart Association has emphasized the importance of moderating sugar intake, advocating for limits on added sugars to maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Moreover, excess sugar consumption is associated with inflammation, which can further exacerbate various medical conditions. People who regularly indulge in sugary beverages and snacks may find themselves caught in a cycle of cravings that makes it increasingly challenging to reduce their intake. By being mindful of the sources of sugar in the diet and opting for whole foods that naturally contain lower levels, individuals can take critical steps toward improving their health outcomes. This shift can also help alleviate the psychological effects that sugar consumption often triggers, such as mood swings and anxiety.
Strategies for Reducing Sugar Intake
Reducing sugar intake is a goal for many who seek better health and wellness. One effective strategy is to gradually cut back on added sugars rather than eliminating them abruptly, which can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms and increased cravings. Instead of going cold turkey, individuals can focus on gradually substituting sugary foods with healthier options. For instance, replacing soda with flavored water or sugary snacks with fresh fruit can satisfy cravings while promoting better health. This approach not only helps to make the transition easier but also encourages a more sustainable lifestyle change that can be maintained over time.
Another practical way to minimize sugar intake is by becoming an expert at reading food labels. Many processed foods contain hidden sugars that can contribute to excessive consumption without consumers even realizing it. By understanding nutritional labels, individuals can make informed choices and avoid products high in added sugars. Additionally, meal prepping and cooking at home allows for greater control over ingredients, helping to ensure meals are delicious yet lower in sugar. Awareness and education about the effects of sugar can empower individuals to make healthier choices, ultimately enhancing their dietary habits and overall well-being.
The Science Behind Sugar Cravings
The science behind sugar cravings delves into the complex interaction between our body’s biochemistry and psychological behavior. When we consume sugar, our bodies release dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Over time, this response can create a conditioning effect, making individuals crave sugar even when they’re not hungry. Eating sugar frequently sets off a cycle of cravings that can be challenging to break. Understanding this biological mechanism can contribute to better strategies for managing these cravings, which often lead to unhealthy eating habits and increased sugar dependence.
Furthermore, research indicates that not all sugars are created equal. Naturally occurring sugars found in whole foods like fruits and vegetables are accompanied by fiber, vitamins, and minerals that provide health benefits. In contrast, processed sugars often lead to rapid spikes in blood glucose levels, which can exacerbate cravings and trigger a cycle of overconsumption. Recognizing this difference can help individuals choose more nutrient-dense foods that satisfy their sweet tooth without contributing to the detrimental effects associated with excessive sugar intake.
How to Manage Sugar Cravings Effectively
Managing sugar cravings effectively involves a combination of behavioral strategies and dietary adjustments. One primary method is to incorporate a balanced diet that includes adequate proteins and healthy fats, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the frequency of cravings. Foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can also assist in curbing cravings by providing a sense of fullness and satisfaction. Being mindful of meal timing and incorporating regular physical activity are additional strategies that can promote moderation in sugar consumption and help individuals resist the temptation to indulge in sugary treats.
Moreover, psychological strategies such as mindfulness and stress management can significantly impact sugar cravings. Stress is a known trigger for many people to reach for comfort foods, particularly those high in sugar. Engaging in activities such as meditation, yoga, or even regular sleep can reduce stress levels and lead to healthier eating patterns. By equipping themselves with the right tools and knowledge, individuals can effectively navigate their cravings and enjoy a balanced approach to sugar consumption that prioritizes their health.
Understanding Processed Sugars and Their Impact
Processed sugars are a prevalent aspect of modern diets, found in everything from snacks to sauces and beverages. These sugars are often added during manufacturing, enhancing flavors without providing any meaningful nutritional benefits. The widespread presence of processed sugars in convenience foods raises concerns about their effects on health. Regular consumption of these sugary products can contribute to weight gain, metabolic disorders, and dental issues, highlighting the importance of reducing intake for overall well-being. Understanding the differences between natural and processed sugars is crucial for healthier dietary choices.
To combat the potential health issues associated with processed sugars, consumers should focus on whole foods and minimize their intake of pre-packaged items. Cooking meals at home using fresh ingredients is an effective way to control sugar levels in the diet, allowing individuals to enjoy sweet flavors naturally found in fruits while avoiding artificial additives. By making informed choices and prioritizing whole foods, individuals can significantly decrease their consumption of processed sugars and foster a healthier lifestyle.
The Balance Between Enjoyment and Health
Finding a balance between enjoying sugary foods and maintaining health is vital in today’s society. It’s essential to recognize that while sugar can enhance the taste of many dishes, excessive consumption can lead to serious health consequences. Moderation is key; allowing oneself the occasional treat can prevent feelings of deprivation that often lead to overindulgence later. Understanding this balance means acknowledging that sugar is not inherently bad, as long as it is integrated mindfully into one’s diet.
Moreover, incorporating naturally sweet alternatives, like fruits, can satisfy sweet cravings while offering additional nutrients and fiber. By focusing on portion control and mindful eating, individuals can enjoy sweets without compromising their health goals. Ultimately, the health implications of sugar come down not just to the choice to consume it, but how it fits into one’s overall lifestyle and dietary habits.
The Psychological Aspects of Sugar Consumption
The psychological aspects of sugar consumption reveal the significance of emotions in our eating habits. Many individuals turn to sugary foods as a source of comfort during stressful times, leading to a cycle of emotional eating. This reliance on sugar for emotional relief can reinforce negative habits and may require psychological intervention alongside dietary change. Understanding the connection between emotions and cravings can empower individuals to develop healthier coping mechanisms that don’t resort to sugary indulgences.
Additionally, it’s important to acknowledge the impact of societal influences and marketing on sugar consumption. The pervasive marketing of sugary products can create an environment that normalizes high sugar intake, making it a challenge for individuals to make healthier choices. Addressing the psychological triggers behind sugar cravings, combined with making informed dietary choices, can lead to sustainable change. By focusing on both the mind and body, individuals can achieve a healthier relationship with sugar and food in general.
Educational Approaches to Reducing Sugar Intake
Educational approaches play a crucial role in reducing sugar intake at the community level. Programs aimed at teaching individuals about nutrition, food labels, and the effects of sugar on health can empower people to make more informed food choices. Workshops that involve cooking demonstrations, meal planning strategies, and nutrition education can equip participants with the tools they need to cut down on processed sugars. Such initiatives can foster a culture of health that transcends individual behavior and impacts entire communities.
Moreover, schools can also play a pivotal role in shaping children’s dietary habits by incorporating nutrition education into their curricula. By teaching kids about the importance of reducing sugar intake and promoting healthier alternatives from a young age, we create a foundation for lifelong healthy eating habits. Such educational approaches create awareness around the dangers of excessive sugar consumption and encourage positive changes in dietary behavior, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive according to scientific research?
While sugar has been shown to increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. However, many people do experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they stop consuming high amounts of processed sugars.
What are the effects of sugar on health in terms of addiction?
The effects of sugar on health can be significant, particularly when consumption includes large amounts of processed sugars. High sugar intake is linked to various health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, which can be influenced by addictive-like eating behaviors.
How do sugar cravings compare to cravings for addictive substances?
Sugar cravings can resemble those for addictive substances in terms of intensity, but they typically do not lead to the same severe withdrawal symptoms. While sugar increases cravings due to its palatability, its addictive potential is less severe than true psychoactive substances.
What are effective strategies for reducing sugar intake?
To reduce sugar intake, individuals can gradually decrease their consumption of processed sugars by reading food labels, opting for whole foods, and incorporating more natural sugars from fruits and vegetables. Going ‘cold turkey’ is often counterproductive.
Do processed sugars have a more addictive quality than natural sugars?
Processed sugars, often found in ultra-processed foods, can have a more addictive quality due to their high palatability and accessibility, which can increase cravings and lead to habitual excessive consumption.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar Cravings | Cravings are genuine, comparable to those experienced with addictive substances. |
| Classification of Sugar | Sugar is not clinically classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Withdrawal Effects | Abruptly stopping sugar can lead to similar withdrawal symptoms, though less severe than drugs. |
| Dietary Needs | Sugar is naturally found in many healthy foods and essential for some diets. |
| Recommended Limits | The American Heart Association suggests limits of 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and even less for children. |
| Moderation is Key | Moderate sugar intake can enhance enjoyment; going cold turkey on sugar may be counterproductive. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This is a contentious topic among nutrition experts. While sugar can induce cravings similar to addictive substances, it does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction. The presence of ultra-processed foods with high sugar contents can lead to habitual consumption and withdrawal symptoms. It’s crucial to recognize that while we do need some sugar in our diets for flavor and energy, moderation is key. The American Heart Association’s guidelines emphasize limiting sugar intake to maintain health, demonstrating that with careful consumption, sugar can be enjoyed without the negative consequences often associated with addiction.